我們(men) 在上篇文章中,已經大概了解了今年全球大部分國家麵臨(lin) 的問題——通貨膨脹。也了解到了在麵臨(lin) 通貨膨脹時,各國政府會(hui) 采取措施來應對高漲的物價(jia) 上升對人們(men) 生活水平帶來的負麵影響。
要解決(jue) 高通貨膨脹,政府的宏觀政策主要有三個(ge) :
① monetary policies-貨幣政策
② fiscal policies-財政政策
③ supply-side policy-總供應相關(guan) 政策
Monetary policies
refers to the use of interest rates, exchange rates and the money supply to control macroeconomic objectives and to affect the level of economic activityMeasures:interest rate, money supply and exchange rate
Fiscal policy
refersthe use of taxes and government spending to affect macroeconomic objectives such as economic growth and employmentMeasures:taxation and government spending
為(wei) 了解決(jue) 由於(yu) 總需求AD上升導致的demand-pull inflation,一般需要使用能夠降低AD的contractionary policy收縮性政策。
a)Contractionary monetarypolicy: increase interest rate, reduce money supply and increase exchange rate
b)Contractionary fiscalpolicy: increase tax rate and reduce government spending
Supply-side
referslong-term measures to increase the productive capacity of the economy, leading to an outward shift of the production possibility curve.Measures:
Education and training
Taxcut
Subsidy
Labour market reforms
Deregulation
Privatisation
Improveinfrastructure
supply-side policy可以通過降低cost of production的方式,來增加aggregated supply,從(cong) 而降低物價(jia) 。主要解決(jue) cost-push inflation。
讓我們(men) 看看在麵臨(lin) 40年來最高通貨膨脹時美國是如何應對的
美國經濟在疫情期間采取寬鬆政策刺激總需求後,經濟有在複蘇,但卻因為(wei) stressed supply chain due to shutdown of china , Russian war with Ukraine, and ongoing pandemic麵臨(lin) 著曆史最高通貨膨脹。通貨膨脹導致油價(jia) ,食品價(jia) 格,房價(jia) ,交通價(jia) 格等上漲,居民的生活成本大幅上升。
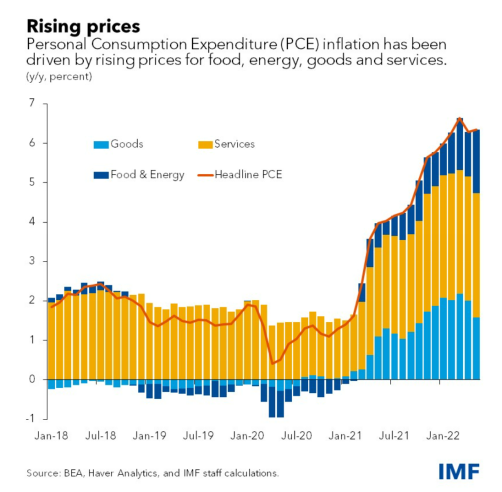
美國主要通過以下四個(ge) 措施來應對高通脹:
1、tighten monetary policy 也就是緊縮的貨幣政策。比如提高利率從(cong) 而減少total demand並遏製價(jia) 格上漲的壓力。今年以來美國加息五次,將聯邦基金利率目標區間上調到3%至3.25%之間。
2、在某些商品上通過price control防止價(jia) 格過高,例如,美國通過白宮3月31日宣布,在未來6個(ge) 月每天從(cong) 戰略石油儲(chu) 備(Strategic Petroleum Reserve)中釋放100萬(wan) 桶,約占全球需求的1%,總釋放量可達到1.8億(yi) 桶。這是白宮有史以來釋放原油儲(chu) 備規模最大的一次。
3、美國還通過改善供應鏈來抑製通脹。減少對中國和俄羅斯的依賴,建立“Indo-Pacific economic Framework”。
4、2022年8月份,美國總統拜登簽署《2022年通脹削減法案》,意在通過減少財政赤字、增加對大企業(ye) 征稅等措施來遏製通脹。
接下來讓我們(men) 運用所學知識於(yu) 題目
Discuss whether monetary policy alone is the best way for a government to correct inflation. [12]
解題思路Part 1define relevant key terms
①Inflation; demand-pull and cost-push.②Monetary policy.
Measures
Contractionary and expansionary
③AD=C+I+G+NX.
Part 2explain how monetary policy could solve inflation
Contractionary monetary policy
Increase interest rate →return of saving decreases→saving decreases→ consume expenditure(C) decrease→ AD decreases.
Increase interest rate→cost of borrowing increases→ investment(I) decreases→ AD decreases.
Increase exchange rate→export becomes relatively more expensive and import becomes relatively cheaper→export decreases and import increases →net export (NX) decreases→AD decreases.
Part 3discuss when the monetary policy is ineffective
The effectiveness of monetary policy to correct inflation will depends on a number of factors:①Interest rate may not solve its problems.
time lag.
a higher interest rate also have adverse effect on unemployment and economic growth.
a rise in the interest rate may discourage foreign investment.
②Confidencelevelmay make consumers’ and investors’ behaviours unpredictable.
Part 4compare to another policy: explain how supply side policy could solve inflation
①Define supply-side policy.
②Explain how the policy measures work.
Increasing spending on education and training→improve labour’s skills (human capital)→productivity increases→AS increases.
Reducing direct tax→such as corporation tax→more profit to increase investment→productivity increases→AS increases.
Privatisation→profit-motive→more efficient→AS increases.
Part 5discuss when the supply-side policy is ineffective
Not very effective in the short term as they can take a long time to have an effect.
increased government spending on education and cuts in tax may increase AD before they increase AS.
Privatisation may not result in an increase in efficiency if the privatized industries become monopolies and do not take into account external costs and benefits.
Part 6evaluate which policy is more likely to be successful
If output and employment are low, LARS perfectly elastic, firm can attract more resources without rising price level, decreasing AD without decreasing the price level.
So contractionary monetary policy can be ineffective.
If economy close to full capacity, LARS vertical, contractionary monetary policy is very effective.
Supply-side policy is effective in the long run but it is time-consuming and costly.
Part 7conclusion















評論已經被關(guan) 閉。